Circuit breakers, fuses and fusible links — general information
Fuses
1. The electrical circuits of the vehicle are protected by a combination of fuses, circuit breakers and fusible links. The main fuse/ relay panel is in the engine compartment (see illustration), while the interior fuse/relay panel is located inside the passenger compartment (see illustration). Each of the fuses is designed to protect a specific circuit, and the various circuits are identified on the fuse panel itself.
i.1a Remove the driver’s dashboard lower cover to expose the under-dash fuse and relay box (on CR-Vs, the under-dash fuse/ relay box is located in the same spot but has an access door in the driver’s dashboard lower cover, so you don’t have to remove the cover)
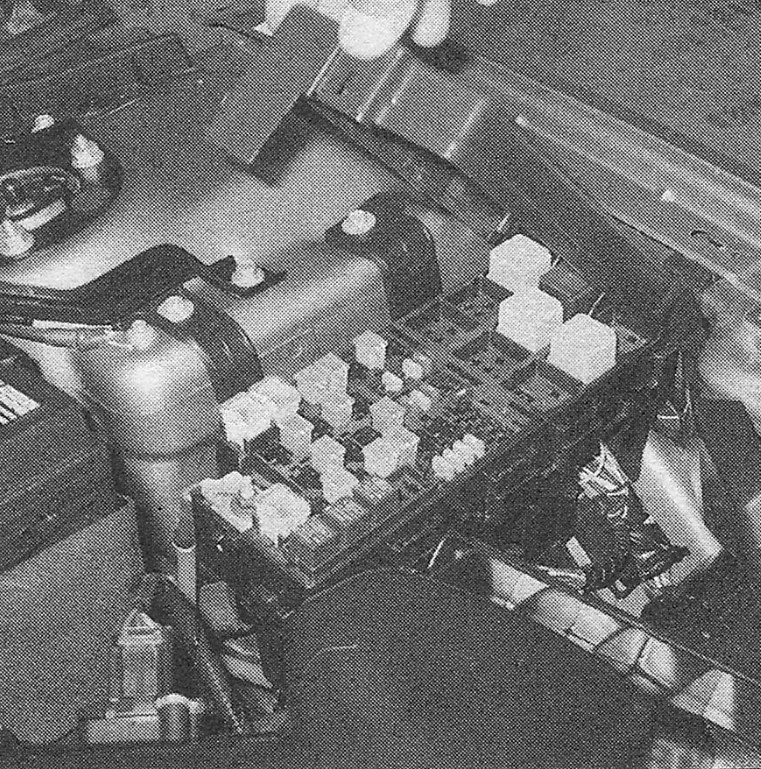

i.1b on coupes and sedans, the engine compartment fuse/relay box is located on the right side of the engine compartment. The functions and locations of the various fuses and relays are listed on the fuse/relay box cover (on CR-Vs and hatchbacks, this fuse/relay box is located on the left side of the engine compartment
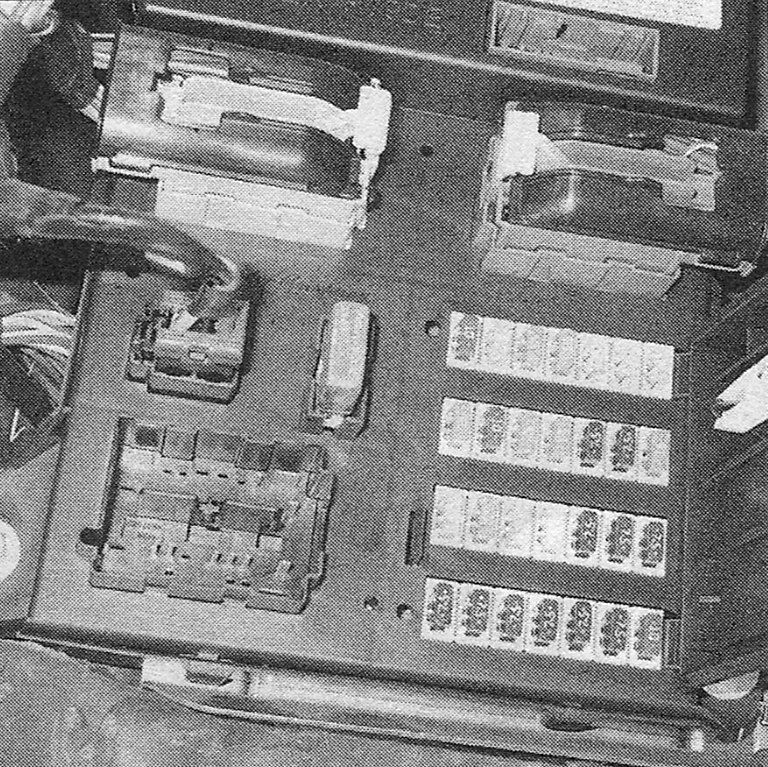

2. Several sizes of fuses are employed in the fuse blocks. There are small, medium and large sizes of the same design, all with the same blade terminal design. The medium and large fuses can be removed with your fingers, but the small fuses require the use of pliers or the small plastic fuse-puller tool found in most fuse boxes.
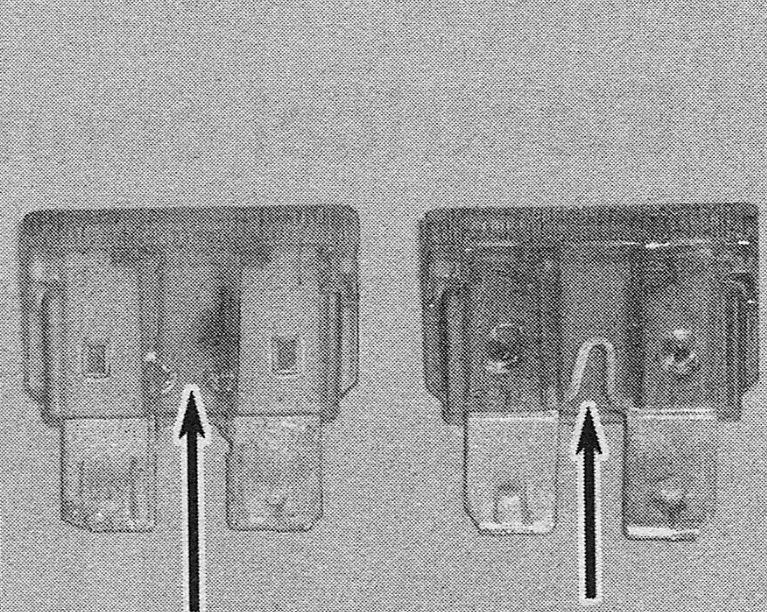
3. If an electrical component fails, always check the fuse first. The best way to check the fuses is with a test light. Check for power at the exposed terminal tips of each fuse. If power is present at one side of the fuse but not the other, the fuse is blown. A blown fuse can also be identified by visually inspecting it (see illustration).
3.3 When a fuse blows, the element between the terminal’s melts
4. Be sure to replace blown fuses with the correct type. Fuses (of the same physical size) of different ratings may be physically interchangeable, but only fuses of the proper rating should be used. Replacing a fuse with one of a higher or lower value than specified is not recommended. Each electrical circuit needs a specific amount of protection. The amperage value of each fuse is molded into the top of the fuse body.
5. If the replacement fuse immediately fails, don’t replace it again until the cause of the problem is isolated and corrected. In most cases, this will be a short circuit in the wiring caused by a broken or deteriorated wire.
Fusible links
6. Some circuits are protected by fusible inks. The links are used in circuits which carry high current.
7. Cartridge-type fusible links are located in the engine compartment fuse/relay box and are similar to a large fuse. After disconnecting the negative battery cable, simply unplug the fusible link and replace it with a fusible link of the same amperage.
Circuit breakers — general information
8. Circuit breakers protect certain circuits, such as the power windows or heated seats. Depending on the vehicle’s accessories, there may be one or two circuit breakers, located in the fuse/relay box in the engine compartment.
9. Because the circuit breakers reset automatically, an electrical overload in a circuit breaker-protected system will cause the car-cult to fail momentarily, then come back on. If the circuit does not come back on, check it immediately.
10. For a basic check, pull the circuit breaker up out of its socket on the fuse panel, but just far enough to probe with a voltmeter. The breaker should still contact the sockets. With the voltmeter negative lead on a good chassis ground, touch each end prong of the circuit breaker with the positive meter probe. There should be battery voltage at each end. If there is battery voltage only at one end, the circuit breaker must be replaced.
11. Some circuit breakers must be reset manually.