Troubleshooting
Fuel pump
1. The fuel pump is located inside the fuel tank. Sit inside the vehicle with the windows closed, turn the ignition key to on (not Start) and listen for the sound of the fuel pump as it’s briefly activated. You will only hear the sound for a second or two, but that sound tells you that the pump is working. Alternatively, have an assistant listen at the fuel filler cap.
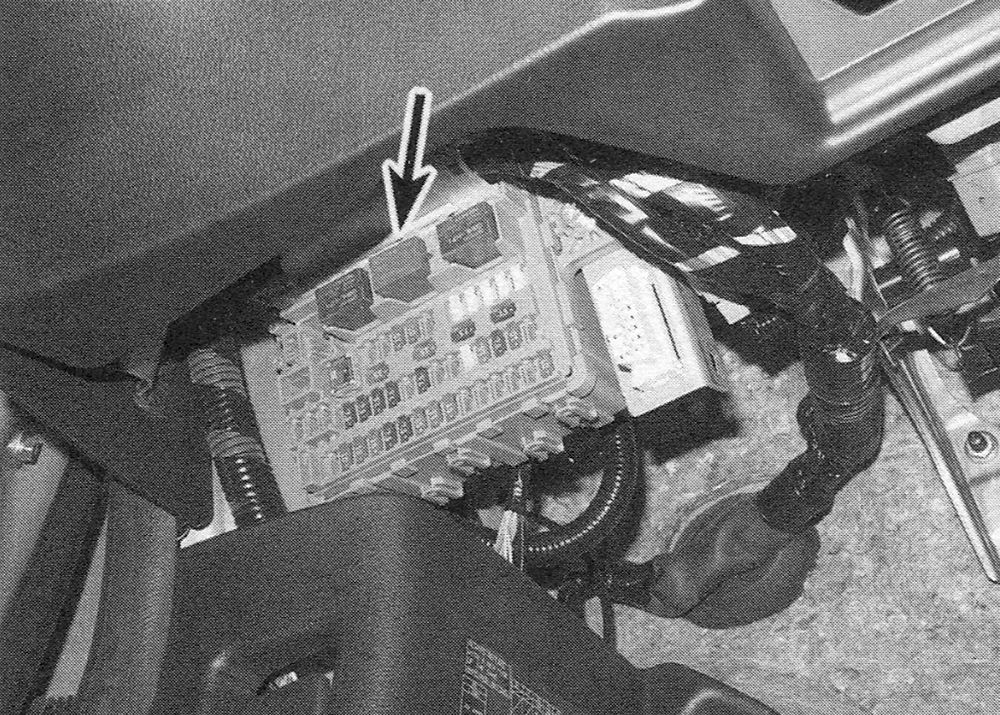
2. If the pump does not come on, check the fuel pump fuse (fuse no. 4 (15A) in the interior fuse/relay box) and the PGM-Fl relay no. 2. The PGM-Fl no. 2 relay is located on the lower part of the interior fuse/relay box (see illustration) and the PGM-Fl no. 1 relay is located at the top of the interior fuse/relay box. If the fuse and relay are okay, check the wiring back to the fuel pump. If the fuse, relay and wiring are okay, the fuel pump is probably defective. If the pump runs continuously with the ignition key in the on position, the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is probably defective. Have the PCM checked by a professional mechanic.
i.2 The PGM-Fl no. 1 and 2 relays are located in the interior fuse/ relay box (2015 Civic shown)
Fuel injection system
Note: The following procedure is based on the assumption that the fuel pump is working and the fuel pressure is adequate (see Fuel pressure — check).
3. Check all electrical connectors that are related to the system. Check the ground wire connections for tightness.
4. Verify that the battery is fully charged (see Engine electrical systems).
5. Inspect the air filter element (see Tune-up and routine maintenance).
6. Check all fuses related to the fuel system (see Chassis electrical system).
7. Check the air induction system between the throttle body and the intake manifold for air leaks. Also inspect the condition of all vacuum hoses connected to the intake manifold and to the throttle body.
8. Remove the air intake duct from the throttle body and look for dirt, carbon, varnish, or another residue in the throttle body, particularly around the throttle plate. If it’s dirty, clean it with carb cleaner, a toothbrush and a clean shop towel.
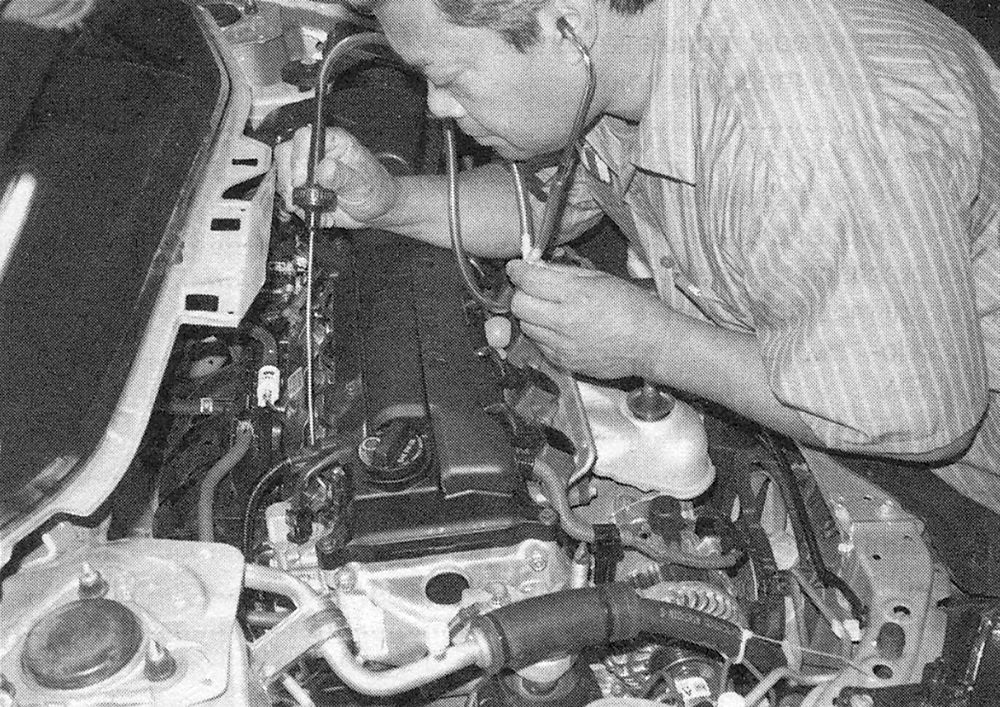
9. With the engine running, place an automotive stethoscope against each injector, one at a time, and listen for a clicking sound that indicates operation (see illustration).
i.9 An automotive stethoscope is used to listen to the fuel injectors in operation

Warning: Stay clear of the drivebelt and any rotating or hot components.
10. If you can hear the injectors operating, but the engine is misfiring, the electrical circuits are functioning correctly, but the injectors might be dirty or clogged. Try a commercial injector cleaning product (available at auto parts stores). If cleaning the injectors doesn’t help, replace the injectors.
11. If an injector is not operating (it makes no sound), disconnect the injector electrical connector and measure the resistance across the injector terminals with an ohmmeter. Compare this measurement to the other injectors. If the resistance of the non-operational injector is quite different from the other injectors, replace it.
12. If the injector is not operating, but the resistance reading is within the range of resistance of the other injectors, the PCM or the circuit between the PCM and the injector might be faulty.